Science
Scientists Date Dinosaur Eggs to 85.91 Million Years Old
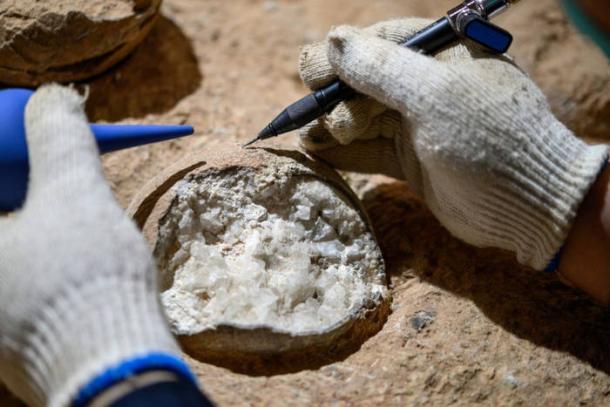

Scientists in China have made a significant advancement in paleontology by successfully dating dinosaur eggs directly for the first time. This research has revealed that the eggs are approximately 85.91 million years old. Conducted at the Qinglongshan site in Hubei Province, this study utilized an innovative “atomic clock” dating technique, which has the potential to reshape our understanding of dinosaur evolution and the climatic conditions of the Late Cretaceous period.
Breakthrough in Dating Techniques
The eggs belong to the species Placoolithus tumiaolingensis, a significant find that provides unique insights into a critical era when Earth’s climate underwent notable changes. The research team, led by Dr. Bi Zhao and published in the journal Frontiers, utilized advanced techniques that have not only dated these fossils but also opened new avenues for analyzing ancient ecosystems.
The eggs were discovered in a clutch of 28 at the Qinglongshan site, a location known for its rich fossil deposits. This breakthrough in dating methods allows scientists to connect the age of these eggs to significant climatic events that may have influenced dinosaur extinction patterns.
Implications for Paleontology
Understanding the timing of these fossils is crucial for piecing together the history of life on Earth, particularly during the Late Cretaceous period. The dramatic cooling of the climate during this time has been linked to various factors affecting global ecosystems, and the eggs provide a tangible record of how these changes may have impacted dinosaur populations.
The work done by the research team represents a shift in how scientists can study ancient life forms. By applying this atomic clock technique, researchers can establish a more detailed timeline of evolutionary events and climatic shifts that shaped the planet during the age of dinosaurs. As scientists continue to uncover the mysteries of these ancient creatures, such advancements in dating methods will be pivotal in understanding their world and eventual extinction.
This groundbreaking research not only enhances our understanding of the past but also demonstrates the potential of new technologies in the field of paleontology. The insights gained from the 85.91 million-year-old eggs could lead to further discoveries that illuminate the complex interplay between climate and life during one of Earth’s most fascinating periods.
-

 Top Stories2 days ago
Top Stories2 days agoTributes Surge for 9-Year-Old Leon Briody After Cancer Battle
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoAimee Osbourne Joins Family for Emotional Tribute to Ozzy
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoDanny Healy-Rae Considers Complaint After Altercation with Garda
-

 Top Stories1 day ago
Top Stories1 day agoNewcastle West Woman Patricia Foley Found Safe After Urgent Search
-
 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoIreland Enjoys Summer Heat as Hurricane Erin Approaches Atlantic
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoHawaii Commemorates 80 Years Since Hiroshima Bombing with Ceremony
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoFianna Fáil TDs Urgently Consider Maire Geoghegan-Quinn for Presidency
-

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day agoConor Murray Reflects on His Career in New Autobiography
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoGaza Aid Distribution Tragedy: 20 Killed Amid Ongoing Violence
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoCouple Convicted of Murdering Two-Year-Old Grandson in Wales
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoClashes Erupt Between Far-Right Groups and Migrants in Spain
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoAristocrat Constance Marten and Partner Convicted of Infant Murder









