Science
Scientists Date Dinosaur Eggs to 85.91 Million Years Using Atomic Clocks
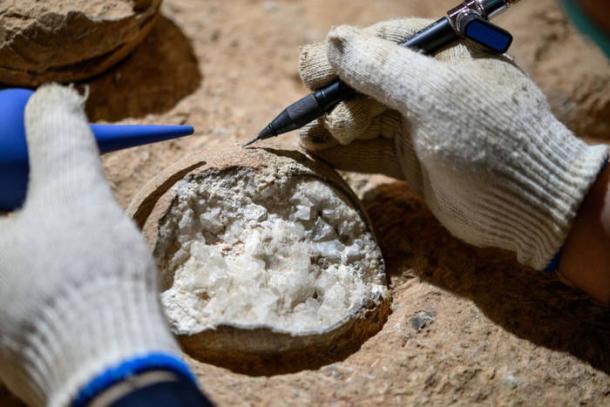

Scientists in China have achieved a significant advancement in paleontology by successfully dating dinosaur eggs directly for the first time. This groundbreaking research, conducted on specimens from the Qinglongshan site in Hubei Province, has revealed that these ancient fossils are approximately 85.91 million years old. The innovative “atomic clock” dating technique employed in this study promises to enhance our understanding of dinosaur evolution and climate changes during the Late Cretaceous period.
New Insights into Dinosaur Evolution
This unprecedented dating of the dinosaur eggs, which belong to the species Placoolithus tumiaolingensis, offers valuable insights into a critical period marked by dramatic climatic shifts. Researchers suggest that the cooling climate may have played a significant role in influencing dinosaur extinction patterns. The clutch of eggs discovered at the Qinglongshan site contains 28 eggs, primarily from the same species, providing a rare glimpse into the reproductive behaviors of these ancient creatures.
The findings, published in the journal Frontiers, reflect a collaboration among prominent paleontologists and geologists, including lead researcher Bi Zhao. “This atomic clock method allows us to pinpoint the age of these fossils with unprecedented precision,” Zhao stated. “Understanding the conditions during the Late Cretaceous will shed light on the factors that led to the extinction of dinosaurs.”
Technological Breakthrough in Paleontology
The atomic clock dating technique marks a significant improvement over traditional methods, which often rely on indirect dating through surrounding geological layers. By utilizing advanced technology, scientists can now achieve greater accuracy in determining the age of fossils. This method may pave the way for future studies aimed at uncovering the life history of dinosaurs and their environment.
The discovery at the Qinglongshan site is part of a broader initiative to explore the fossil record in China, which has yielded numerous significant finds in recent years. As the research continues, paleontologists hope to uncover more about the ecological systems that existed during the time of the dinosaurs, including the impact of climate on their survival.
The implications of this study extend beyond academic interest; they resonate with broader concerns regarding climate change today. By examining how ancient species responded to climatic shifts, scientists can draw parallels to current environmental challenges. The research not only enriches our knowledge of the past but also provides context for understanding the ongoing dynamics of life on Earth.
As paleontology evolves with new techniques and technologies, the potential for further discoveries remains vast. The successful dating of dinosaur eggs at the Qinglongshan site stands as a testament to the innovative spirit of scientific inquiry and its ability to unveil the mysteries of our planet’s distant past.
-

 Top Stories4 days ago
Top Stories4 days agoTributes Surge for 9-Year-Old Leon Briody After Cancer Battle
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoAimee Osbourne Joins Family for Emotional Tribute to Ozzy
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoConor Murray Reflects on His Career in New Autobiography
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoDanny Healy-Rae Considers Complaint After Altercation with Garda
-

 Top Stories3 days ago
Top Stories3 days agoNewcastle West Woman Patricia Foley Found Safe After Urgent Search
-
 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoIreland Enjoys Summer Heat as Hurricane Erin Approaches Atlantic
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoHawaii Commemorates 80 Years Since Hiroshima Bombing with Ceremony
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoFianna Fáil TDs Urgently Consider Maire Geoghegan-Quinn for Presidency
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoGaza Aid Distribution Tragedy: 20 Killed Amid Ongoing Violence
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoCouple Convicted of Murdering Two-Year-Old Grandson in Wales
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoClashes Erupt Between Far-Right Groups and Migrants in Spain
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoAristocrat Constance Marten and Partner Convicted of Infant Murder









