Health
Men Require Double the Exercise of Women for Heart Health
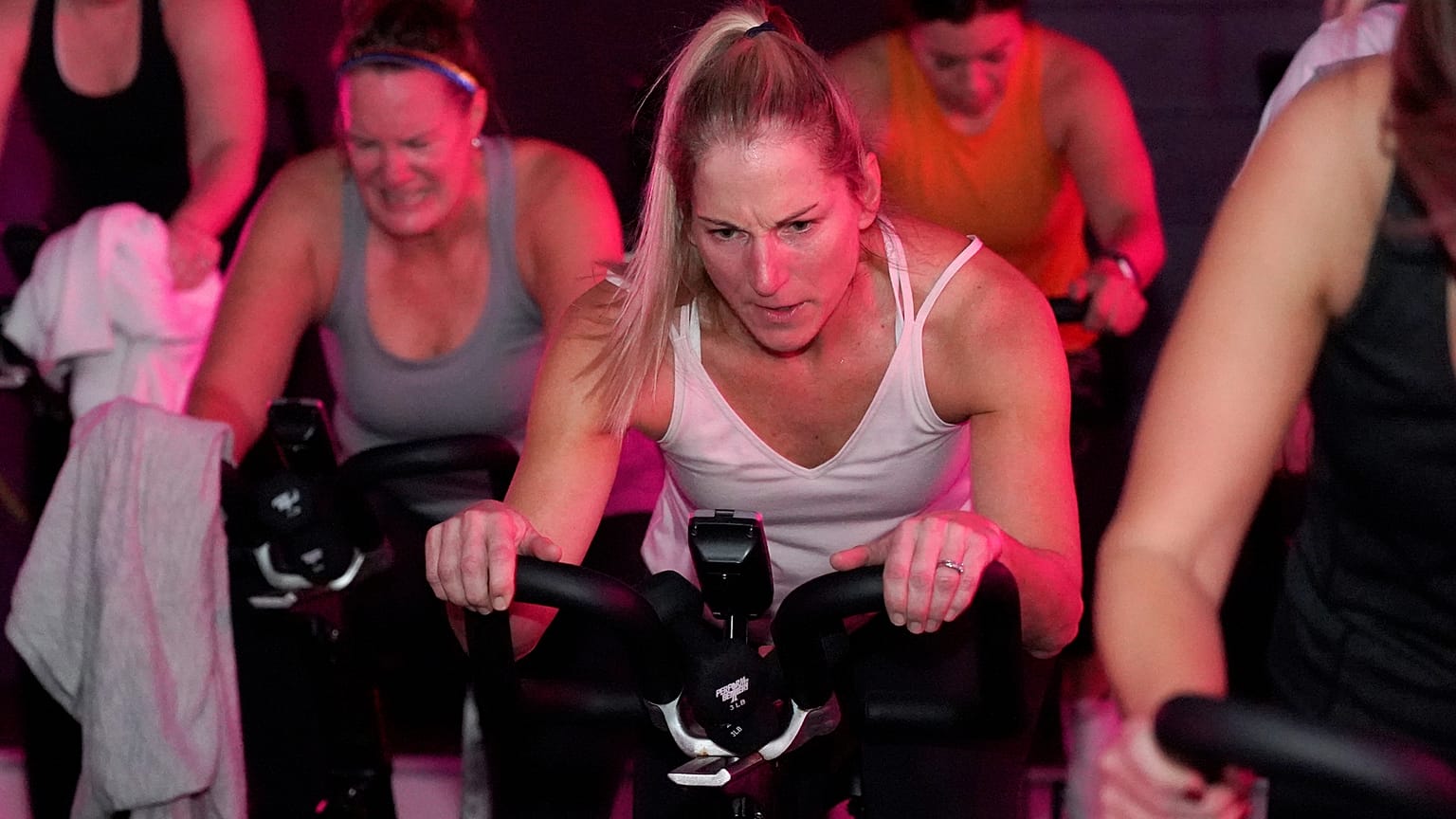
A recent study has revealed that men need to engage in nearly twice the amount of exercise as women to achieve equivalent benefits for heart health. The findings, published in the journal Nature Cardiovascular Research, indicate that while a modest amount of physical activity can enhance cardiovascular health, men must significantly increase their exercise duration to reap similar rewards as women.
Women who exercise for approximately four hours each week can reduce their risk of developing coronary heart disease by an average of 30 percent. In comparison, men require almost nine hours of exercise weekly to experience the same level of risk reduction. This discrepancy highlights a significant gender difference in the relationship between exercise and heart health.
Coronary heart disease is characterized by the constriction or calcification of heart vessels, which diminishes blood supply to the heart. Risk factors include an unhealthy diet, insufficient physical activity, and smoking. The study emphasizes that even lower levels of exercise can yield health benefits; for instance, around 2.5 hours of moderate to vigorous activity per week can decrease the risk of coronary heart disease by 22 percent for women and 17 percent for men.
The results surprised Karl Lauterbach, former health minister of Germany, who expressed his discontent on social media, describing the findings as “unfair.” The research also demonstrated that individuals with existing heart disease can gain advantages from physical activity. Women who engage in moderate to vigorous exercise for at least 51 minutes weekly experienced a reduced risk of mortality, while men required approximately 85 minutes to achieve the same survival benefit. This means men must exercise around 1.7 times as much as women to gain equivalent health outcomes.
Biological Factors Behind the Disparity
The study suggests that biological differences may account for the observed disparities in exercise benefits between genders. Women possess a natural advantage due to the hormone oestrogen, which aids in fat-burning and offers protective effects on blood vessels. Additionally, women generally have a higher proportion of endurance-oriented muscle fibers, while men typically have more power-oriented muscle fibers. These physiological characteristics could help explain why women experience improved heart health with less training.
Overall, the research underscores the importance of regular physical activity in reducing the risk of heart disease for both men and women. Increased frequency of exercise correlates with a lower likelihood of developing cardiovascular issues, regardless of gender. These insights may prompt a reevaluation of exercise recommendations tailored to individual needs and biological differences.
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoTributes Surge for 9-Year-Old Leon Briody After Cancer Battle
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoAimee Osbourne Joins Family for Emotional Tribute to Ozzy
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoDanny Healy-Rae Considers Complaint After Altercation with Garda
-
 Top Stories4 months ago
Top Stories4 months agoIreland Enjoys Summer Heat as Hurricane Erin Approaches Atlantic
-

 World5 months ago
World5 months agoHawaii Commemorates 80 Years Since Hiroshima Bombing with Ceremony
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoNewcastle West Woman Patricia Foley Found Safe After Urgent Search
-

 Top Stories5 months ago
Top Stories5 months agoFianna Fáil TDs Urgently Consider Maire Geoghegan-Quinn for Presidency
-

 World5 months ago
World5 months agoCouple Convicted of Murdering Two-Year-Old Grandson in Wales
-

 World5 months ago
World5 months agoGaza Aid Distribution Tragedy: 20 Killed Amid Ongoing Violence
-

 World5 months ago
World5 months agoAristocrat Constance Marten and Partner Convicted of Infant Murder
-

 Top Stories4 months ago
Top Stories4 months agoClimbing Errigal: A Must-Do Summer Adventure in Donegal
-

 Top Stories4 months ago
Top Stories4 months agoHike Donegal’s Errigal Mountain NOW for Unforgettable Summer Views









