World
NASA’s Perseverance Rover Detects Electrical Activity on Mars
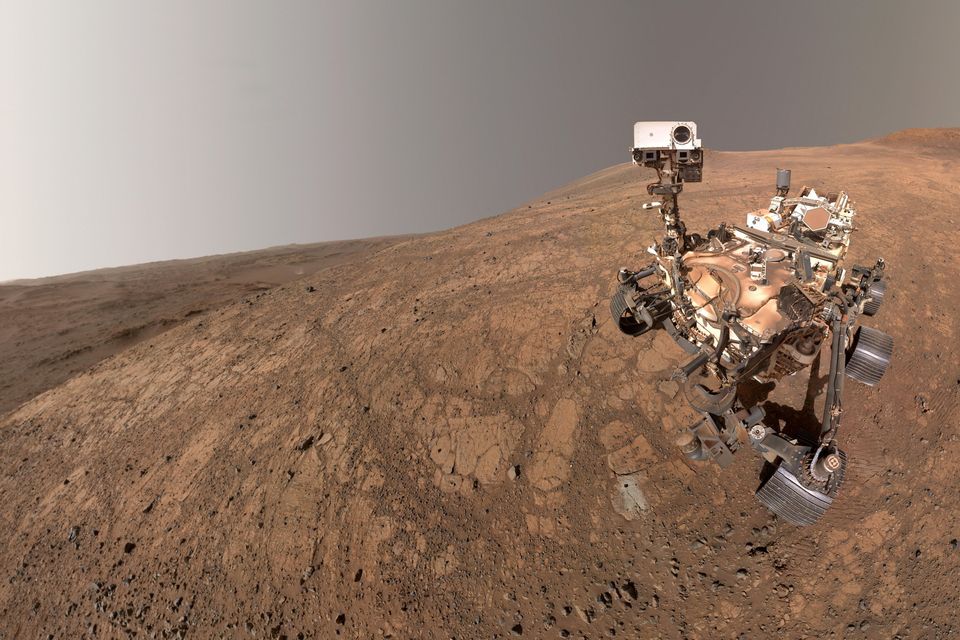

NASA’s Perseverance rover has made a significant discovery, revealing that the atmosphere of Mars is electrically active. This finding emerged from audio and electromagnetic recordings collected by the rover’s SuperCam instrument during its exploration of Jezero Crater, located in the northern hemisphere of Mars, since 2021.
Baptiste Chide, a planetary scientist at the Institute for Research in Astrophysics and Planetology in France, emphasized the implications of this discovery, stating, “These discharges represent a major discovery, with direct implications for Martian atmospheric chemistry, climate, habitability, and the future of robotic and human exploration.” He noted that the electrical charges responsible for these discharges could significantly influence dust transport on Mars, a critical process that remains poorly understood.
The findings stem from an analysis of 28 hours of microphone recordings made by the rover over the course of two Martian years. During this period, researchers detected a total of 55 electrical discharges, which are typically associated with dust devils. These discharges were not lightning in the conventional sense; rather, they were described as “mini-lightning,” characterized by brief sparks measuring just a few millimeters long.
According to Ralph Lorenz, a planetary scientist and co-author of the study from the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, “We did not detect lightning by the common definition. It sounded like a spark or whip-crack.” The electrical phenomena occur when tiny dust grains collide and generate friction in the Martian atmosphere, resulting in the buildup of electrons that discharge as electrical arcs.
Understanding Martian Dust Devils
Sixteen of the recorded discharges happened during two close encounters with dust devils. Dust devils are prevalent on Mars, as confirmed by another study published in October 2023, which reported wind speeds reaching up to 158 km/h. The internal dynamics of these dust devils contribute to the generation of electrical discharges.
Chide explained that these small-scale electrical phenomena are created by the friction of dust grains, which accumulate electrons and subsequently release their charge as arcs several centimeters long, producing audible shockwaves. “I would call it ‘mini-lightning’,” he added, highlighting the unique nature of the events observed.
The electrical activity in Mars’ atmosphere had been suspected for some time, but this research marks a breakthrough in confirming it. Lorenz stated, “What we’ve observed is a result of having exceptionally sensitive instrumentation observing for a long period, so we can detect very small discharges, about the energy of an automobile ignition.”
This discovery not only enhances our understanding of Mars’ atmospheric processes but also raises concerns regarding the potential risks these electrical discharges pose to the electronic equipment of current robotic missions. Moreover, they could present hazards for future astronauts exploring the Red Planet.
The ongoing analysis of data from the Perseverance rover will continue to shed light on the complexities of Martian weather and its implications for future exploration, both robotic and human. As scientists delve deeper into these findings, the mysteries of Mars’ atmosphere are gradually being unraveled, paving the way for a better understanding of the Red Planet’s environmental conditions.
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoTributes Surge for 9-Year-Old Leon Briody After Cancer Battle
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoAimee Osbourne Joins Family for Emotional Tribute to Ozzy
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoDanny Healy-Rae Considers Complaint After Altercation with Garda
-
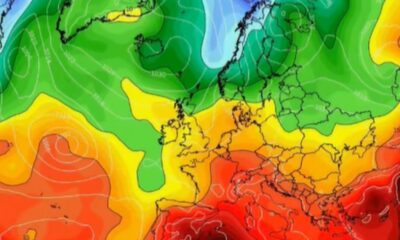
 Top Stories4 months ago
Top Stories4 months agoIreland Enjoys Summer Heat as Hurricane Erin Approaches Atlantic
-

 World5 months ago
World5 months agoHawaii Commemorates 80 Years Since Hiroshima Bombing with Ceremony
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoNewcastle West Woman Patricia Foley Found Safe After Urgent Search
-

 Top Stories5 months ago
Top Stories5 months agoFianna Fáil TDs Urgently Consider Maire Geoghegan-Quinn for Presidency
-

 World5 months ago
World5 months agoCouple Convicted of Murdering Two-Year-Old Grandson in Wales
-

 World5 months ago
World5 months agoGaza Aid Distribution Tragedy: 20 Killed Amid Ongoing Violence
-

 World5 months ago
World5 months agoAristocrat Constance Marten and Partner Convicted of Infant Murder
-

 Top Stories4 months ago
Top Stories4 months agoClimbing Errigal: A Must-Do Summer Adventure in Donegal
-

 Top Stories4 months ago
Top Stories4 months agoHike Donegal’s Errigal Mountain NOW for Unforgettable Summer Views