Health
Scientists Unveil AI Tool to Predict Genetic Disease Risks
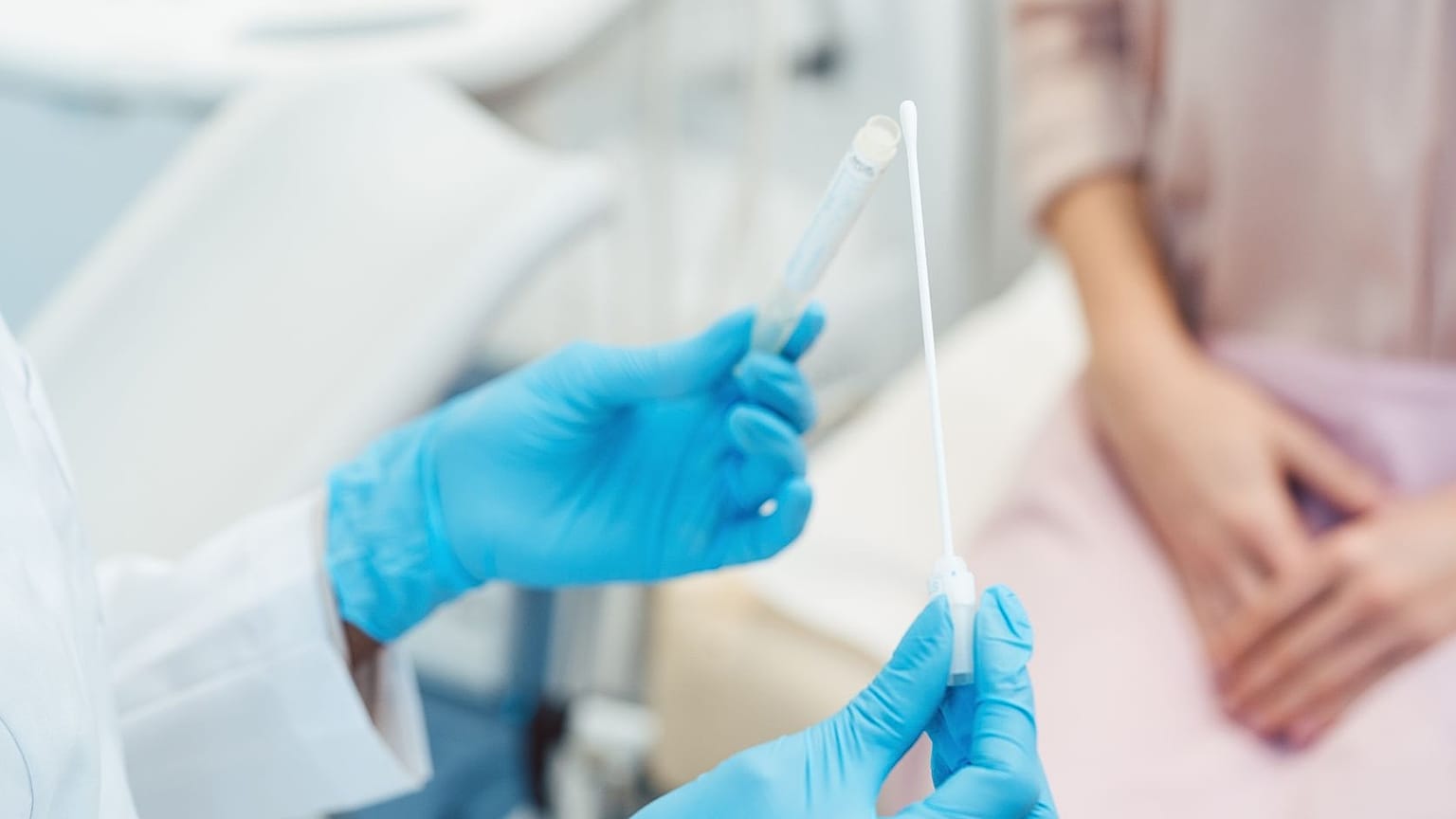
A team of researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York has developed an innovative artificial intelligence (AI) tool designed to enhance the prediction of genetic risks for common hereditary diseases. This advancement aims to assist healthcare professionals in interpreting genetic test results and guiding patients to the appropriate level of medical care.
The AI model focuses on accurately predicting whether rare genetic mutations will result in disease, thereby facilitating early detection while minimizing unnecessary treatments. Genetic testing can identify various changes, or variants, in a person’s DNA, but many of these variants have minimal or no effect on health. Furthermore, a single variant rarely provides a complete understanding of an individual’s risk, as multiple genes and environmental factors contribute to conditions such as heart disease and cancer.
Enhancing Genetic Risk Assessment
To address these challenges, the New York-based research team utilized more than one million electronic health records to create AI models targeting ten inherited conditions, including breast cancer and polycystic kidney disease (PKD). The researchers assigned a score between 0 and 1 to patients with rare genetic variants, quantifying their likelihood of developing specific diseases. This comprehensive approach enabled the team to calculate risk scores for over 1,600 genetic variants.
Ron Do, a professor of personalized medicine and one of the study’s authors, emphasized the importance of this tool in providing clarity in genetic testing outcomes. “We wanted to move beyond black-and-white answers that often leave patients and providers uncertain about what a genetic test result actually means,” he stated. By integrating AI with real-world laboratory data, such as cholesterol levels and blood counts, the model aims to provide a more nuanced risk assessment for individuals with particular genetic variants.
Guiding Clinical Decisions
The findings, published in the journal Science, suggest that the AI tool could significantly impact clinical practice. The model has already revealed connections between certain genetic mutations and disease risks that were previously categorized as “uncertain.” Dr. Iain Forrest, the study’s lead author, noted, “While our AI model is not meant to replace clinical judgment, it can potentially serve as an important guide, especially when test results are unclear.”
The risk scores produced by the AI could help physicians determine whether patients require additional screenings or interventions, while also reducing the anxiety associated with low-risk variants. “This approach allows us to avoid unnecessary worry or intervention if the variant is low-risk,” Forrest added.
Looking ahead, the researchers plan to expand the model to encompass a broader range of diseases and genetic variants, while also including a more diverse patient population. “Ultimately, our study points to a potential future where AI and routine clinical data work hand in hand to provide more personalized, actionable insights for patients and families navigating genetic test results,” Do concluded.
This development represents a significant step towards leveraging technology in healthcare, aiming to improve patient outcomes through more informed decision-making based on genetic information.
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoTributes Surge for 9-Year-Old Leon Briody After Cancer Battle
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoAimee Osbourne Joins Family for Emotional Tribute to Ozzy
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoDanny Healy-Rae Considers Complaint After Altercation with Garda
-
 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoIreland Enjoys Summer Heat as Hurricane Erin Approaches Atlantic
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoHawaii Commemorates 80 Years Since Hiroshima Bombing with Ceremony
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoNewcastle West Woman Patricia Foley Found Safe After Urgent Search
-

 Top Stories4 months ago
Top Stories4 months agoFianna Fáil TDs Urgently Consider Maire Geoghegan-Quinn for Presidency
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoGaza Aid Distribution Tragedy: 20 Killed Amid Ongoing Violence
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoCouple Convicted of Murdering Two-Year-Old Grandson in Wales
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoAristocrat Constance Marten and Partner Convicted of Infant Murder
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoClimbing Errigal: A Must-Do Summer Adventure in Donegal
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoHike Donegal’s Errigal Mountain NOW for Unforgettable Summer Views









