Science
Scientists Date Dinosaur Eggs to 85.91 Million Years with New Method
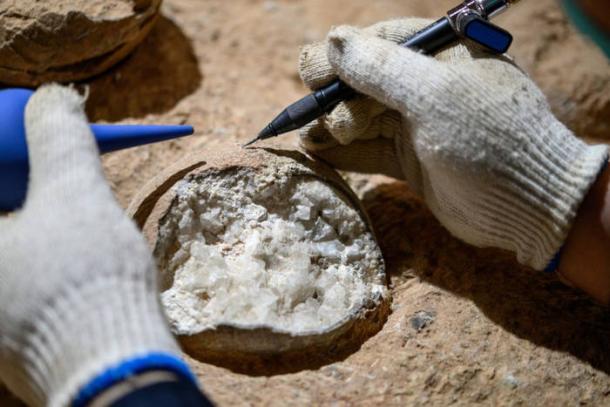

Scientists in China have made a significant advancement in paleontology by directly dating dinosaur eggs for the first time, revealing them to be approximately 85.91 million years old. This breakthrough was achieved through research conducted at the Qinglongshan site in Hubei Province, utilizing a novel “atomic clock” dating technique. The findings promise to enhance our understanding of dinosaur evolution and the climate changes that occurred during the Late Cretaceous period.
Revolutionary Dating Technique
The research team employed an innovative approach that enables precise dating of fossils, marking a departure from traditional methods that often rely on indirect dating or geological context. This atomic clock method measures the decay of isotopes within the eggs, providing an accurate timeline for when these ancient creatures laid their eggs.
The dinosaur eggs belong to the species Placoolithus tumiaolingensis, which are of particular interest due to their implications for understanding the Earth’s climatic shifts during a critical period. The Late Cretaceous was characterized by significant cooling events that may have played a role in the extinction patterns of dinosaurs.
Insights into a Critical Period
The clutch of eggs discovered at the Qinglongshan site consists of 28 specimens, with the majority identified as Placoolithus tumiaolingensis. These fossils not only provide a glimpse into the reproductive behavior of dinosaurs but also serve as vital indicators of the environmental conditions they faced.
Research into this age of dinosaurs is essential for piecing together the complex puzzle of their extinction. The cooling climate during the Late Cretaceous likely affected food sources and habitats, contributing to the challenges faced by these ancient reptiles.
The findings from this study have been published in the journal Frontiers, highlighting the importance of modern techniques in paleontological research. The implications of accurately dating these fossils extend beyond academic interest; they may also inform current understandings of climate change and its impacts on biodiversity.
Overall, this achievement in dating dinosaur eggs represents a promising step forward in the field of paleontology. As scientists continue to explore the depths of our planet’s history, breakthroughs like these offer invaluable insights into the life that once roamed Earth millions of years ago.
-

 Top Stories4 days ago
Top Stories4 days agoTributes Surge for 9-Year-Old Leon Briody After Cancer Battle
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoAimee Osbourne Joins Family for Emotional Tribute to Ozzy
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoConor Murray Reflects on His Career in New Autobiography
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoDanny Healy-Rae Considers Complaint After Altercation with Garda
-

 Top Stories3 days ago
Top Stories3 days agoNewcastle West Woman Patricia Foley Found Safe After Urgent Search
-
 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoIreland Enjoys Summer Heat as Hurricane Erin Approaches Atlantic
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoHawaii Commemorates 80 Years Since Hiroshima Bombing with Ceremony
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoFianna Fáil TDs Urgently Consider Maire Geoghegan-Quinn for Presidency
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoGaza Aid Distribution Tragedy: 20 Killed Amid Ongoing Violence
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoCouple Convicted of Murdering Two-Year-Old Grandson in Wales
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoClashes Erupt Between Far-Right Groups and Migrants in Spain
-

 Top Stories3 days ago
Top Stories3 days agoPatrick Kielty Returns to Late Late Show, Thanks Supporters









